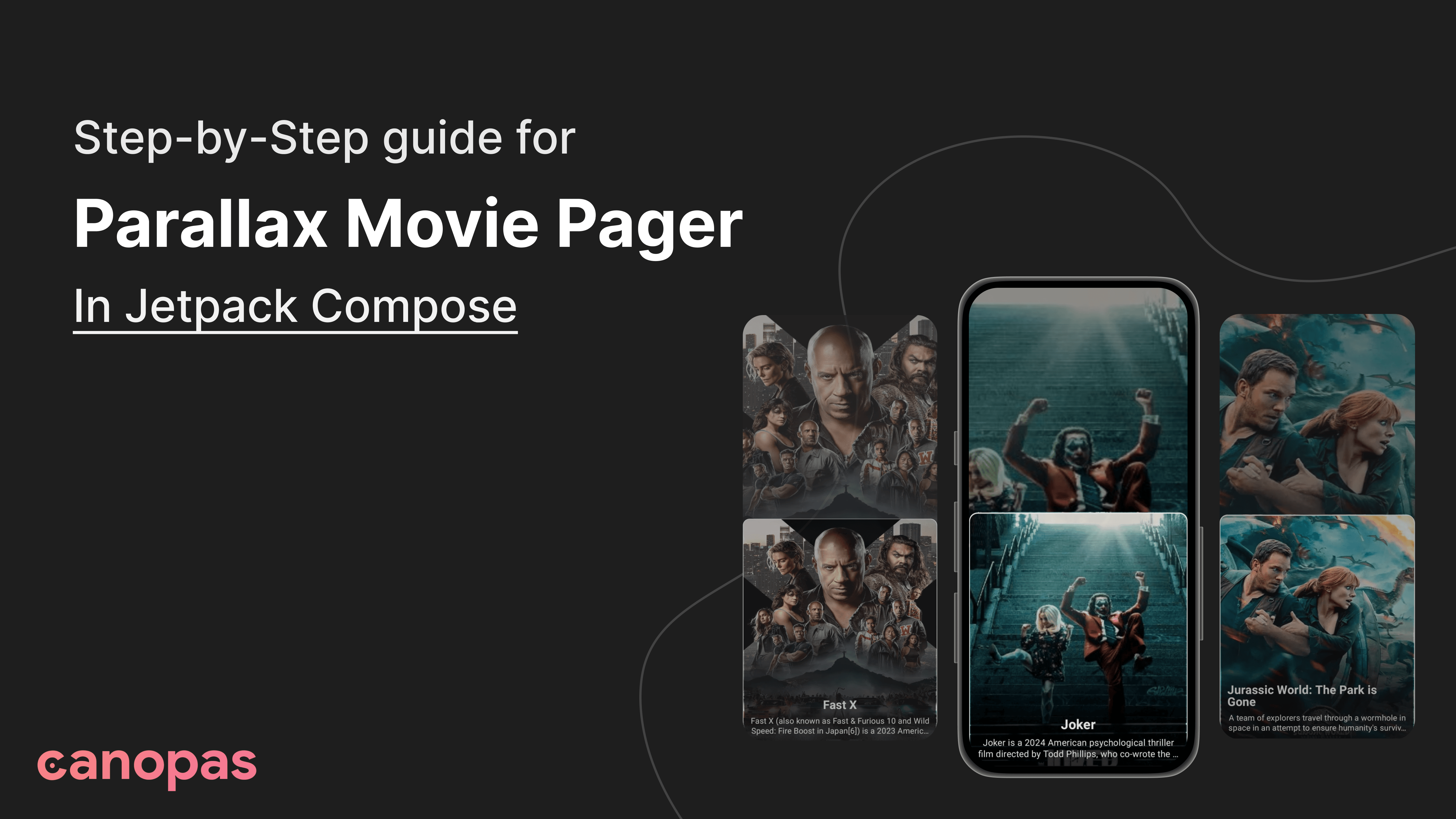
How To Create a Parallax Movie Pager In Jetpack Compose
Introduction
Parallax animations can make any app interface stand out by adding depth and interactivity. In this blog post, we'll build a movie pager with a cool parallax effect using Jetpack Compose. You'll learn how to create smooth scrolling effects, synchronize two pagers, and animate movie cards and images in a way that brings your app to life.
The source code is available on GitHub.
This blog is also available as a YouTube video, feel free to check it out.
Overview of the Implementation
We will create a movie pager that displays a background image that moves at a different speed than the foreground content, creating a depth effect. Our implementation will consist of two main components:
- Background Image Pager: Displays the movie poster images.
- Movie Cards Pager: Shows movie details over the background images.
Let’s start implementing it step-by-step…
Step 1: Setting Up Your Jetpack Compose Project
First, we need to create a new Jetpack Compose project.
- Open Android Studio: Select "New Project," and choose the "Empty Compose Activity" template.
- Name Your Project: Give your project a suitable name that reflects its purpose.
- Ensure Dependencies: Make sure you have the latest dependencies for Jetpack Compose in your project.
1. Update libs.versions.toml
In your libs.versions.toml file, ensure you have the following lines under the [versions] section to specify the Coil version:
coil = "2.7.0"Next, add the Coil libraries under the [libraries] section:
coil = { group = "io.coil-kt", name = "coil", version.ref = "coil" }
coil-compose = { group = "io.coil-kt", name = "coil-compose", version.ref = "coil" }2. Update build.gradle.kts
In your build.gradle.kts file, include the Coil dependencies by adding the following lines in the dependencies block:
dependencies {
// Other dependencies...
implementation(libs.coil) // Add Coil for image loading
implementation(libs.coil.compose) // Add Coil for Compose support
}3. Sync Your Project
After adding the dependencies, make sure to sync your Gradle files so that the changes take effect.
Step 2: Gradient Overlay and Utility Functions
We’ll create a gradient overlay for better readability and define utility functions for calculating offsets and loading images.
@Composable
private fun GradientOverlay() {
Box(
modifier = Modifier
.fillMaxSize()
.background(
Brush.verticalGradient(
listOf(Color.Black.copy(alpha = 0.6f), Color.Transparent),
startY = 0f,
endY = 500f
)
)
)
}
fun calculatePageOffset(state: PagerState, currentPage: Int): Float {
return (state.currentPage + state.currentPageOffsetFraction - currentPage).coerceIn(-1f, 1f)
}Translation and Scaling Calculations
We’ll be using below concepts for calculating translation values and scaling values:
- calculatePageOffset: This function calculates the offset of the current page relative to the state of the pager. It considers both the current page and the fraction of the page being scrolled, normalizing the value to a range between -1 and 1.
- Translation Calculations:
lerp(30f, 0f, 1f - currentPageOffset): This line interpolates between 30 and 0 based on the current page offset, allowing the background image to move from right to left as you scroll. For movie cards,lerp(100f, 0f, 1f - currentPageOffset)calculates how much to translate the card based on its position in the pager. - Scale Calculations:
lerp(0.8f, 1f, 1f - currentPageOffset.absoluteValue.coerceIn(0f, 1f)): This calculates the scale of the movie card, scaling it from 0.8 to 1.0 as it approaches the center of the screen. - Parallax Effect: The parallax effect is achieved by multiplying the
currentPageOffsetbyscreenWidth * 2fto create a greater movement effect, making the background image scroll slower than the foreground content.
Step 3: Setting Up the UI Structure
We start by creating a MoviePager composable function, which will house both the background and foreground elements.
@Composable
fun MoviePager(paddingValues: PaddingValues) {
val backgroundPagerState = rememberPagerState(pageCount = { movies.size })
val movieCardPagerState = rememberPagerState(pageCount = { movies.size })
// Derived state to track scrolling status
val scrollingFollowingPair by remember {
derivedStateOf {
when {
backgroundPagerState.isScrollInProgress -> backgroundPagerState to movieCardPagerState
movieCardPagerState.isScrollInProgress -> movieCardPagerState to backgroundPagerState
else -> null
}
}
}
// Synchronizing scrolling of two pagers
LaunchedEffect(scrollingFollowingPair) {
scrollingFollowingPair?.let { (scrollingState, followingState) ->
snapshotFlow { scrollingState.currentPage + scrollingState.currentPageOffsetFraction }
.collect { pagePart ->
val (page, offset) = BigDecimal.valueOf(pagePart.toDouble())
.divideAndRemainder(BigDecimal.ONE)
.let { it[0].toInt() to it[1].toFloat() }
followingState.requestScrollToPage(page, offset)
}
}
}
// Layout for both pagers
Box(
modifier = Modifier
.fillMaxSize()
.padding(paddingValues),
contentAlignment = Alignment.TopCenter
) {
BackgroundImagePager(backgroundPagerState)
GradientOverlay()
MovieCardsPager(movieCardPagerState)
}
}Step 4: Implementing the Background Image Pager
The BackgroundImagePager displays the background images and applies a translation effect based on the current page offset.
@Composable
private fun BackgroundImagePager(state: PagerState) {
HorizontalPager(
modifier = Modifier.fillMaxSize(),
state = state
) { currentPage ->
// Get the current page offset
val currentPageOffset = calculatePageOffset(state, currentPage)
// Calculate the translation for the background image
val translationX = lerp(30f, 0f, 1f - currentPageOffset)
Box(Modifier.fillMaxSize()) {
Image(
painter = rememberAsyncImagePainter(movies[currentPage].url),
contentDescription = movies[currentPage].title,
contentScale = ContentScale.FillBounds,
modifier = Modifier
.fillMaxSize()
.graphicsLayer { this.translationX = translationX } // Apply translation
)
}
}
}Step 5: Creating the Movie Cards Pager
The MovieCardsPager shows the details of the movies on top of the background images. Each movie card has its own scaling and translation based on the current page offset.
@Composable
private fun MovieCardsPager(state: PagerState) {
HorizontalPager(
modifier = Modifier.fillMaxSize(),
state = state,
verticalAlignment = Alignment.Bottom
) { currentPage ->
val context = LocalContext.current
val coroutineScope = rememberCoroutineScope()
var imageBitmap by remember { mutableStateOf<ImageBitmap?>(null) }
LaunchedEffect(currentPage) {
loadImageBitmap(context, coroutineScope, movies[currentPage].url) {
imageBitmap = it.asImageBitmap()
}
}
// Get the current page offset
val currentPageOffset = calculatePageOffset(state, currentPage)
MovieCard(currentPage, imageBitmap, currentPageOffset)
}
}Step 6: Designing the Movie Card
The MovieCard composable displays the movie image and details while applying transformations for the parallax effect.
@Composable
private fun MovieCard(currentPage: Int, imageBitmap: ImageBitmap?, currentPageOffset: Float) {
// Calculate translation and scaling based on the current page offset
// Translate the card on the X-axis
val cardTranslationX = lerp(100f, 0f, 1f - currentPageOffset)
// Scale the card on the X-axis
val cardScaleX = lerp(0.8f, 1f, 1f - currentPageOffset.absoluteValue.coerceIn(0f, 1f))
Box(
modifier = Modifier
.fillMaxWidth()
.fillMaxHeight(0.7f)
.graphicsLayer {
scaleX = cardScaleX // Apply scaling
translationX = cardTranslationX // Apply translation
}
.background(Color.Black, shape = MaterialTheme.shapes.large)
) {
imageBitmap?.let {
ParallaxImage(imageBitmap, currentPageOffset)
}
MovieCardOverlay(currentPage, currentPageOffset)
}
}Step 7: Implementing the Parallax Image Effect
The ParallaxImage composable uses a Canvas to draw the image with a parallax offset based on the current page offset.
@Composable
private fun ParallaxImage(imageBitmap: ImageBitmap, currentPageOffset: Float) {
val drawSize = IntSize(imageBitmap.width, imageBitmap.height)
val screenWidth = LocalConfiguration.current.screenWidthDp
// Calculate parallax offset
val parallaxOffset = currentPageOffset * screenWidth * 2f
Canvas(
modifier = Modifier
.fillMaxSize()
.clip(MaterialTheme.shapes.large)
.border(2.dp, Color.White, MaterialTheme.shapes.large)
.graphicsLayer { translationX = lerp(10f, 0f, 1f - currentPageOffset) } // Apply translation
) {
translate(left = parallaxOffset) {
drawImage(
image = imageBitmap,
srcSize = drawSize,
dstSize = size.toIntSize(),
)
}
}
}Step 8: Overlaying Movie Details
In the MovieCardOverlay, we display the movie title and description with translation and opacity effects based on the current page offset.
@Composable
private fun BoxScope.MovieCardOverlay(currentPage: Int, currentPageOffset: Float) {
// Overlay background and text details
Box(
modifier = Modifier
.fillMaxSize()
.padding(4.dp)
.clip(MaterialTheme.shapes.large)
.background(
Brush.verticalGradient(
listOf(Color.Transparent, Color.Black.copy(alpha = 0.8f)),
startY = 500f,
endY = 1000f
)
)
)
Column(
modifier = Modifier
.align(Alignment.BottomCenter)
.offset(y = -(20).dp),
horizontalAlignment = Alignment.CenterHorizontally
) {
// Title translations and animations
val titleTranslationX = lerp(30f, 0f, 1f - currentPageOffset.absoluteValue.coerceIn(0f, 1f)) // Translate title
val titleAlpha = lerp(0f, 1f, 1f - currentPageOffset.absoluteValue.coerceIn(0f, 1f)) // Set title opacity
Text(
text = movies[currentPage].title,
style = MaterialTheme.typography.titleMedium.copy(
color = Color.White,
fontSize = 24.sp,
fontWeight = FontWeight.Bold
),
modifier = Modifier
.padding(horizontal = 16.dp, vertical = 8.dp)
.graphicsLayer {
translationX = titleTranslationX // Apply translation
alpha = titleAlpha // Apply opacity
}
)
// Description translations and animations
val descriptionTranslationX = lerp(150f, 0f, 1f - currentPageOffset.absoluteValue.coerceIn(0f, 1f)) // Translate description
val descriptionAlpha = lerp(0f, 1f, 1f - currentPageOffset.absoluteValue.coerceIn(0f, 1f)) // Set description opacity
Text(
text = movies[currentPage].description,
style = MaterialTheme.typography.bodyMedium.copy(
color = Color.White,
fontSize = 16.sp,
fontWeight = FontWeight.Normal
),
maxLines = 2,
overflow = TextOverflow.Ellipsis,
textAlign = androidx.compose.ui.text.style.TextAlign.Center,
modifier = Modifier
.padding(horizontal = 16.dp)
.graphicsLayer {
translationX = descriptionTranslationX // Apply translation
alpha = descriptionAlpha // Apply opacity
}
)
}
}And that’s it! We have achieved the parallax effect in our UI!
The Source code is available on GitHub.
Conclusion
In this post, we implemented a beautiful parallax effect in a movie pager using Jetpack Compose. By following the steps outlined above, you can create engaging interfaces that captivate users with smooth animations and stunning visuals. Feel free to customize the parameters and styles to suit your app’s theme and happy coding!!

